Recently, several interesting data processing issues have been discovered when I try to use wind speed as IV.
Meteorological data are mostly presented in the form of numerous txt files (like the following figure). Each txt files represents various meteorological values of a weather station within a certain period of time. The simplest way to obtain the mean or quantile of specified variables in all weather stations is to open these txt files one by one and run the solution code. But when we have lots of files, it becomes difficult for us to traverse them manually.

Thus, I’ll show you how to achieve one-time calculations for a certain variable on multiple files with Python.
Introduction of Data
1.Overview
This is more than three million pieces of ground meteorological data provided by 400 meteorological observation stations in China in 2017.
Time range: Most are in three-hour units, and a few have one-hour data.
Meteorological parameters: temperature, air pressure, dew point, wind direction, wind speed, cloud cover and precipitation
2.Objective
Get the average wind speed of the all meteorological data.
Data Analysis
Take one meteorological data as an example, the ninth column is the wind speed we want to analysis. -9999 in each column represents missing values.
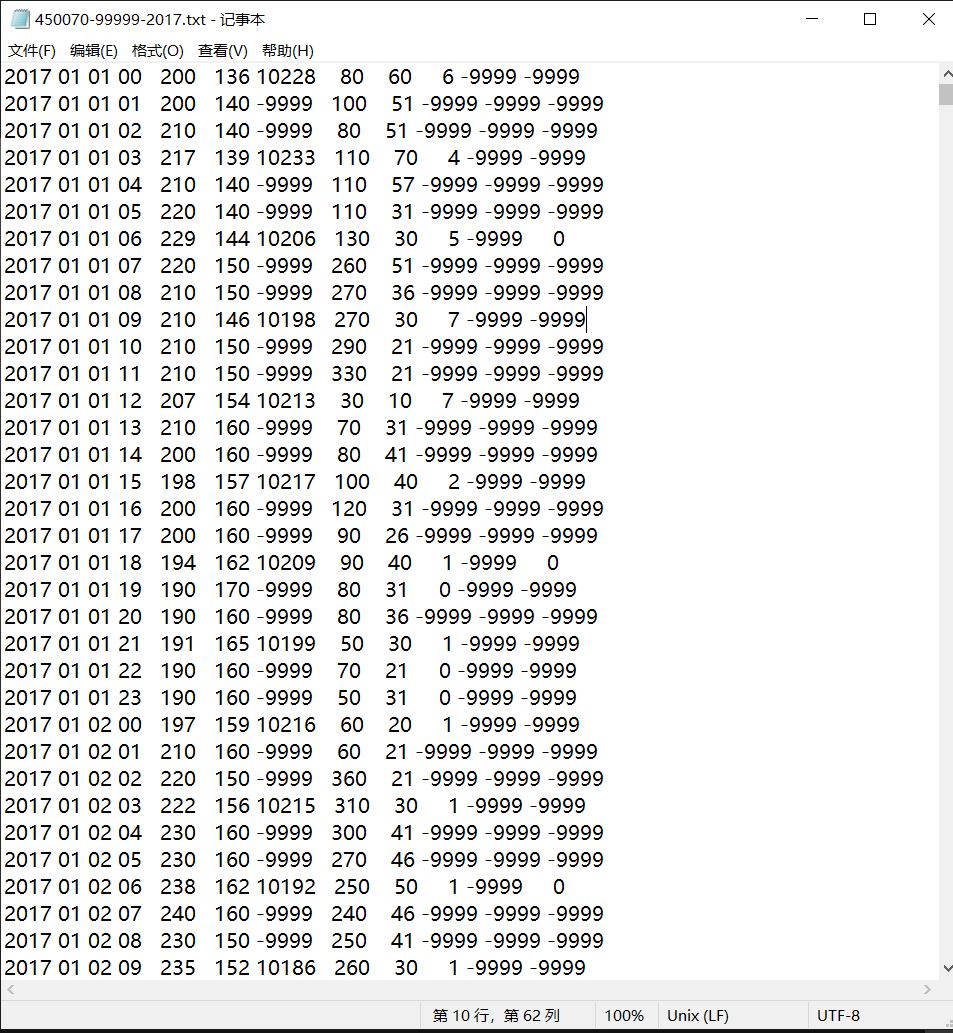
We can analysis it as a csv file:
import os
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
listx=[]
os.chdir('absolute path to data storage')
for filename in os.listdir(os.getcwd()): #read all files in a folder
listxappend(filename)
for i in range(412):
f=pd.read_csv(listx[i],delim_whitespace=True,header=None) #read files with whitespace as delimiter
f=f.replace(-9999,0) #deal with missing value
a1=f.iloc[:,8]
a2=np.mean(a1)
print(a2)
Run the above codes, the results will be:
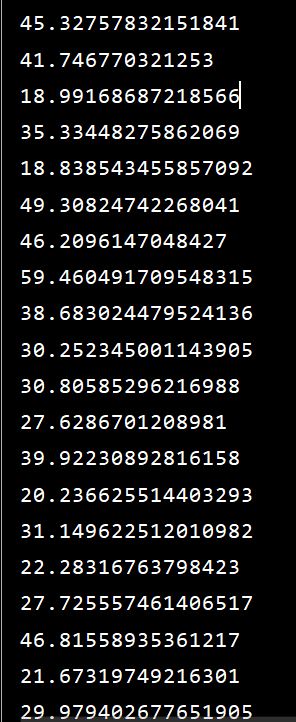
That means we have successfully calculate the average wind speed of the all meteorological data.